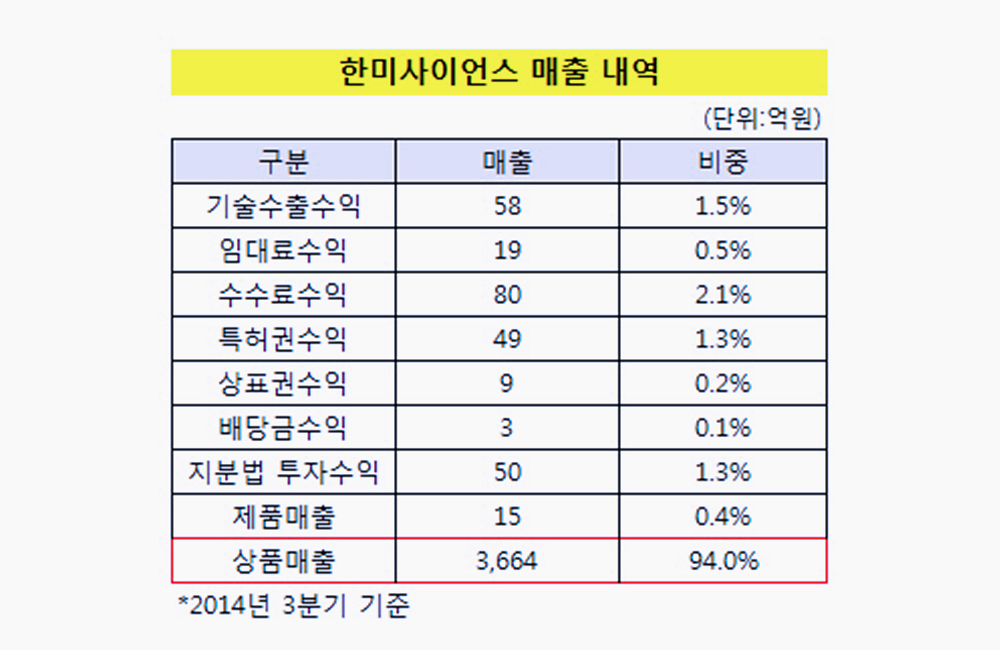
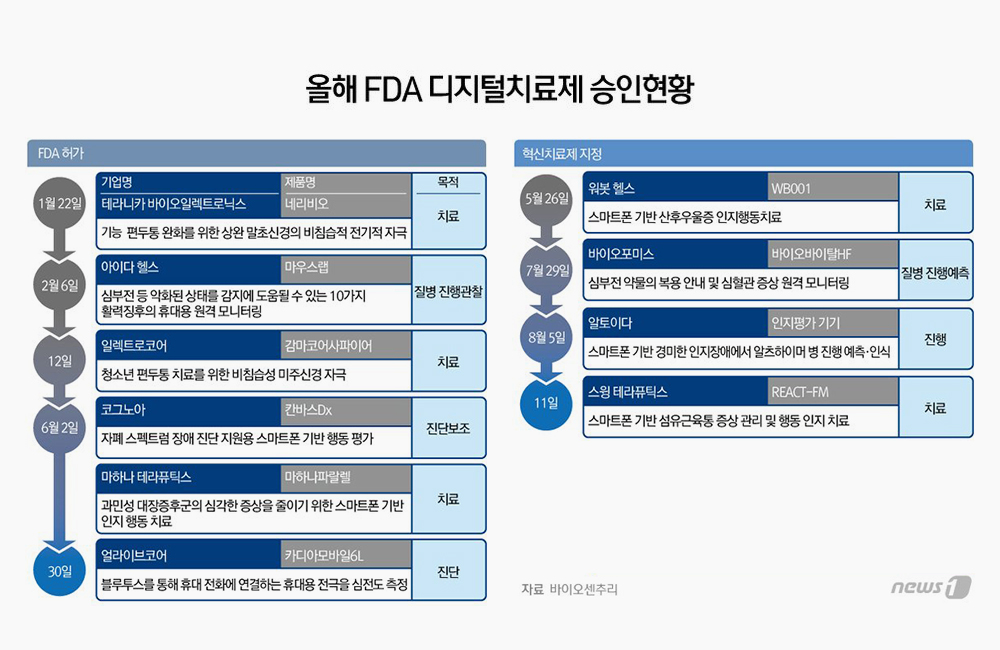
Medical coding is a dynamic and complex field requiring expertise in medical terminology, anatomy and treatments, as well as a deep understanding of billing regulations and practices. With 95,000-plus codes from three medical coding systems, coders play a critical role in a hospital's revenue cycle and financial health. However, the demand for certified coders has significantly increased, especially since the COVID-19 pandemic, leading to a notable shortage in this crucial profession.
The High Stakes of Medical Coding
The medical coder shortage is a critical concern, with the American Medical Association reporting a 30% gap in this vital workforce.[1] This shortfall extends beyond clinical roles, significantly hindering the revenue cycle and finance capabilities in a health system. In fact, a survey by the Healthcare Financial Management Association (HFMA) highlights that 50% of Chief Financial Officers find it increasingly challenging to fill these essential positions in the current labor market.[2]
A shortage of skilled medical coders can cause significant backlogs, delayed claim submissions, errors and reduced reimbursement. This can lead to burnout, causing a vicious cycle of staff shortages. A 2023 AHIMA report found that 48% of respondents experienced decreased reimbursement and slower claims processing due to understaffing.[3]
Medical coding's complexity is evident in procedures such as laceration repairs, where coders must consider details like repair complexity, wound location and involved tissues, among other information. This example mirrors the broader range of coding challenges across different medical scenarios, from routine visits to complex surgeries. Each case demands a deep understanding of the diverse coding guidelines that impact financial, compliance and patient care reporting outcomes. Accuracy is also vital, with a national benchmark of 95%, for proper billing and avoiding issues like insurance denials. The expected productivity varies among coders, with standards based on the number of patient charts reviewed and claims coded. However, simple numerical benchmarks do not capture the complexities inherent in subspecialty coding processes.
The Game-Changing Impact of AI on Administration and Revenue
AI in healthcare is a game-changer. The US spends 34% of healthcare expenses on administrative costs.[4] AI solutions are expected to save the industry $150 billion by 2026.[5] Newer AI models such as Large Language Models (LLM) and Machine Learning (ML) have already improved coding productivity, efficiency and accuracy, lessening the administrative burden on providers.
With today’s rapid technological advancements, PULSE by CorroHealth is a remarkable example of AI’s powerful technological capabilities. PULSE is CorroHealth's next-generation, AI-driven medical coding automation platform that employs LLMs, ML, and algorithmic logic to simplify the coding process, making it nearly touchless. Health systems using PULSE have seen a four to seven-times increase in productivity, allowing more charts to be coded in a day than is humanly possible. Furthermore, PULSE has acquired a thorough understanding of the 95,000+ codes in use, the hospital's payer contracts and industry regulations. This knowledge base enables PULSE to apply the codes accurately, achieving up to a 97 percent accuracy rate, which is above the national benchmark. The system also addresses coding complexity with modules such as Injections and Infusions and Evaluation and Management.
PULSE has already positively impacted a major U.S. health system struggling with complex emergency medical coding challenges. Their old system was inefficient, leaving the staff with a heavy workload and causing a revenue decline. After implementing PULSE, the health system's coding accuracy rate increased from 85.5% to an impressive 98% for emergency procedures. Since its implementation in 2020, the health system has experienced a significant improvement in revenue. The net revenue per patient increased by an extraordinary $30.25, a growth of 23%. As a result, the health system has claimed $504 million in new revenue.
This magic was realized thanks to the health system’s deep collaboration with CorroHealth, forging a partnership based on trust and shared goals. The synergy with PULSE led to transformative results, improving the health system's operations, and setting them on a path toward improved financial integrity and resilience for an excellent future, marking a new era in revenue integrity.
Sources:
[1]. AMA - https://www.ama-assn.org/about/leadership/addressing-another-health-care-shortage-medical-coders
[2]. HFMA - https://www.hfma.org/guidance/healthcare-2030/workforce-of-the-future-empowered-more-diverse-and-vulnerable-to-technology
[3]. AHIMA - https://www.ahima.org/news-publications/press-room-press-releases/2023-press-releases/health-information-workforce-shortages-persist-as-ai-shows-promise-ahima-survey-reveals
[4]. National Library of Medicine - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9628307
[5]. Science Direct - https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2211883722000089